On March 15, 2022, President Biden signed the Cyber Incident Reporting for Critical Infrastructure Act into law, included as part of the Congressional Omnibus Appropriations bill. The law requires critical infrastructure owners and operators to quickly notify the Cyber and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) of ransomware payments and significant cyber-attacks.
The Cyber Incident Reporting for Critical Infrastructure Act creates two new reporting requirements:
- an obligation to report certain cyber incidents to DHS CISA within 72 hours
- an obligation to report ransomware payments within 24 hours
Supporting the new law, Darktrace AI accelerates the cyber incident reporting process. Specifically, Darktrace’s Cyber AI Analyst understands the connections among disparate security incidents with supervised machine learning and autonomously writes incident reports in human-readable language using natural language processing (NLP). These Darktrace incident reports allow human analysts to send reports to CISA quickly and efficiently.
In the below real-world attack case study, we demonstrate how Cyber AI Analyst facilitates seamless reporting for critical infrastructure organizations that fall victim to ransomware and malicious data exfiltration. The AI technology, trained on human analyst behavior, replicates investigations at machine speed and scale, surfacing relevant details in minutes and allowing security teams to understand what happened precisely and share this information with the relevant authorities.
The below threat investigation details a significant threat find on a step by step level in technical detail to demonstrate the power and speed of Cyber AI Analyst.
Cyber AI Analyst’s incident report
When ransomware struck this organization, Cyber AI Analyst was invaluable, autonomously investigating the full scope of the incident and generating a natural language summary that clearly showed the progression of the attack.

In the aftermath of this attack, Darktrace’s technology also offered analyst assistance in mapping out the timeline of the attack and identifying what files were compromised, helping the security team identify anomalous activity related to the ransomware attack.

With Darktrace AI’s insights, the team easily identified the timeline of the attack, affected devices, credentials used, file shares accessed, files exfiltrated, and malicious endpoints contacted, enabling the customer to disclose the scale of the attack and notify necessary parties.
This example demonstrates how Cyber AI Analyst empowers critical infrastructure owners and operators to swiftly report major cyber-attacks to the federal government. Considering that 72 hours is the reporting period is for significant incidents — and 24 hours for ransomware payments — Cyber AI Analyst is no longer a nice-to-have but a must-have for critical infrastructure.
Attack breakdown: Ransomware and data exfiltration
Cyber AI Analyst delivered the most critical information in an easy-to-read report — with no human touch involved — as shown in the incident report above. We will now break down the attack further to demonstrate how Darktrace’s Self-Learning AI understood the unusual activity throughout the attack lifecycle.
In this double extortion ransomware, attackers exfiltrated data over 22 days. The detections made by Darktrace’s Self-Learning AI, and the parallel investigation by Cyber AI Analyst, were used to map the attack chain and identify how and what data had been exfiltrated and encrypted.
The attack consisted of three general groups of events:
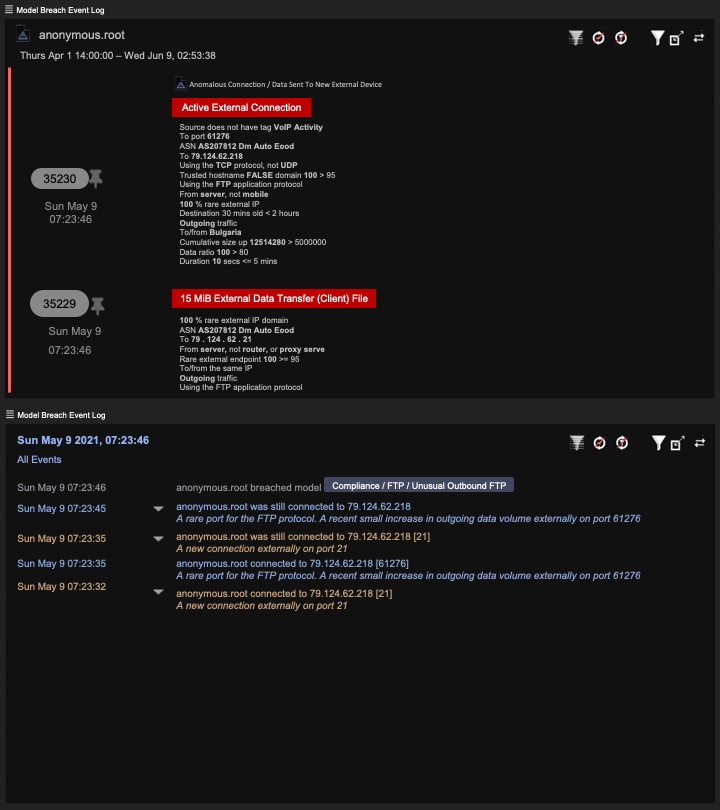
- Unencrypted FTP (File Transfer Protocol) data exfiltration to rare malicious external endpoint in Bulgaria (May 9 07:23:46 UTC – May 21 03:06:46 UTC)
- Ransomware encryption of files in network file shares (May 25 01:00:27 UTC – May 30 07:09:53 UTC)
- Encrypted SSH (Secure Shell) data exfiltration to rare malicious external endpoint (May 29 16:43:37 UTC – May 30 13:23:59 UTC)

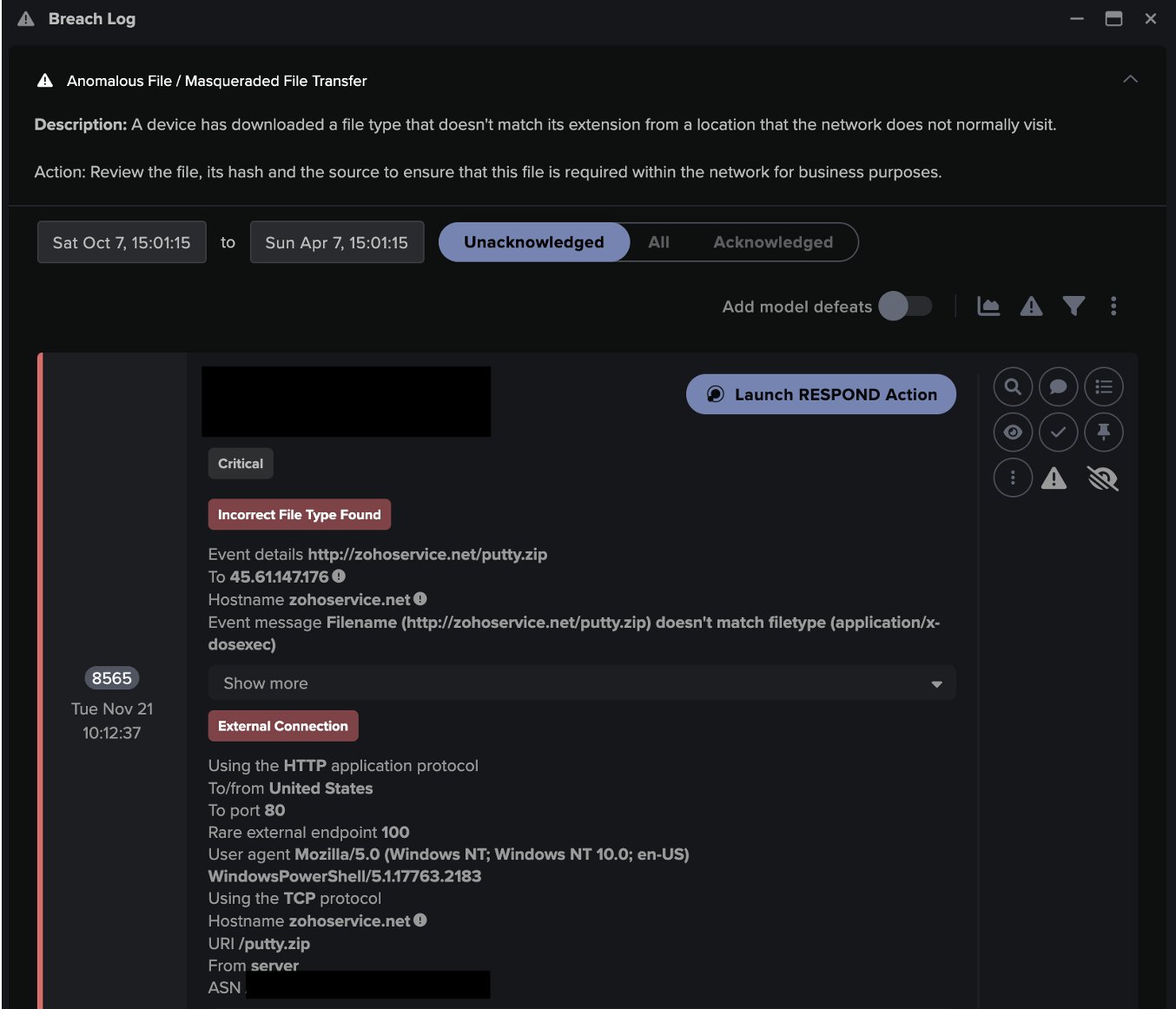
First, uploads of internal data to a rare external endpoint in Bulgaria were observed within the networks. The exfiltration was preceded by SMB reads of internal file shares before approximately 450GB of data was exfiltrated via FTP.
Darktrace’s AI identified this threatening activity on its own, and the organization was quickly able to pinpoint what data had been exfiltrated, including files camouflaged by markings such as ‘Talent Acquisition’ and ‘Engineering and Construction,’ and legal and financial documents — suggesting that these were documents of an extremely sensitive nature.

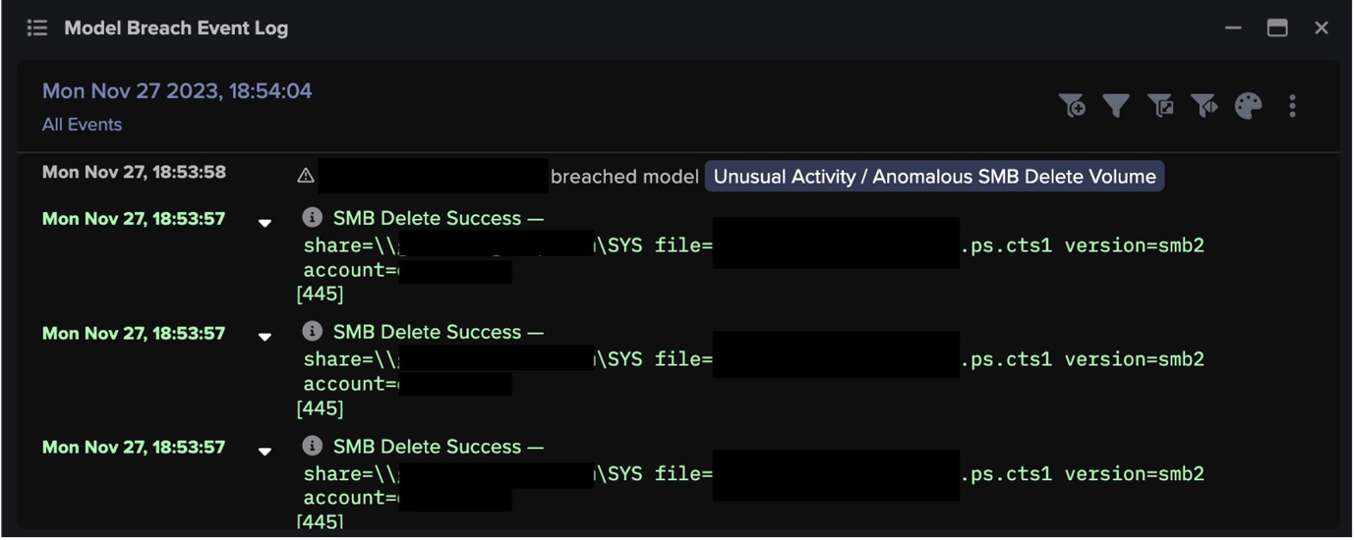
Model breaches:
- Anomalous Connection / Unusual Incoming Data Volume
- Anomalous File / Internal / Additional Extension Appended to SMB File
- Compromise / Ransomware / Suspicious SMB Activity
- Compromise / Ransomware / SMB Reads then Writes with Additional Extensions
- Unusual Activity / Anomalous SMB Move & Write
- Unusual Activity / High Volume Server Data Transfer
- Unusual Activity / Sustained Anomalous SMB Activity
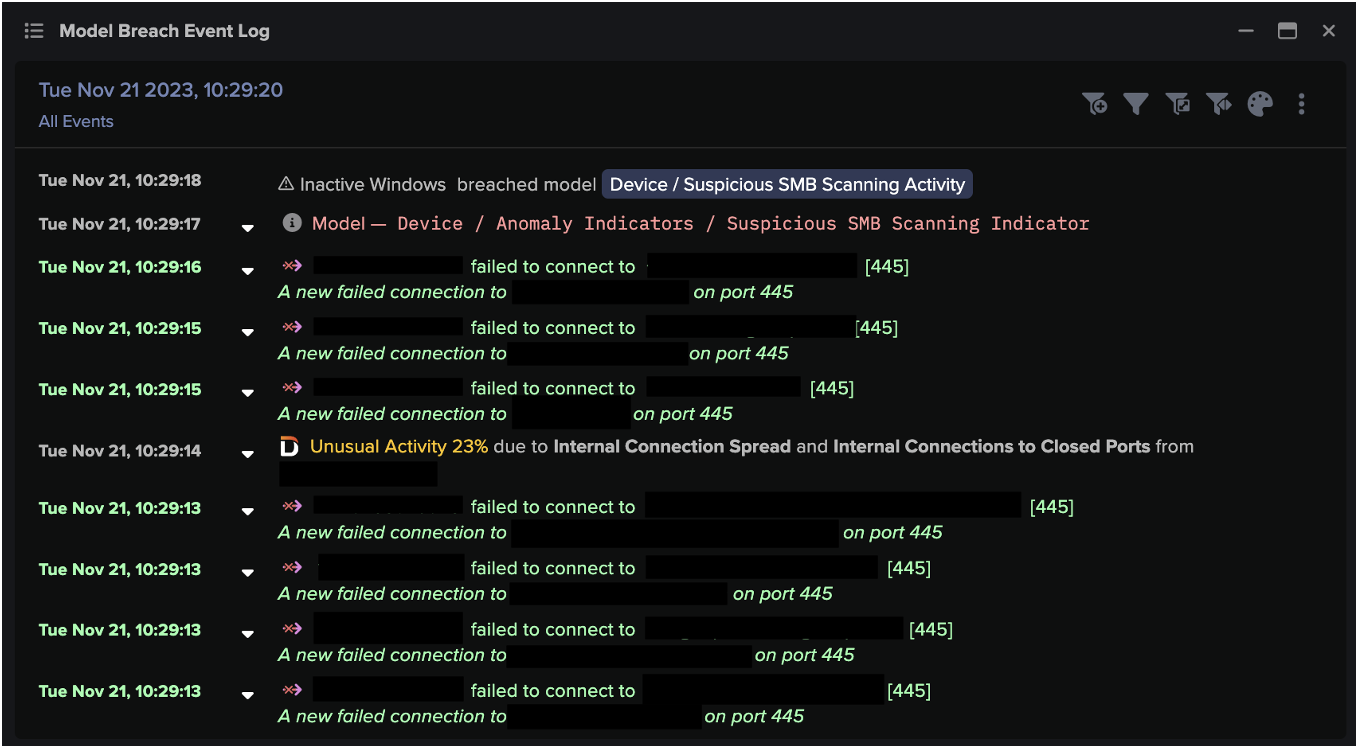
- Device / SMB Lateral Movement
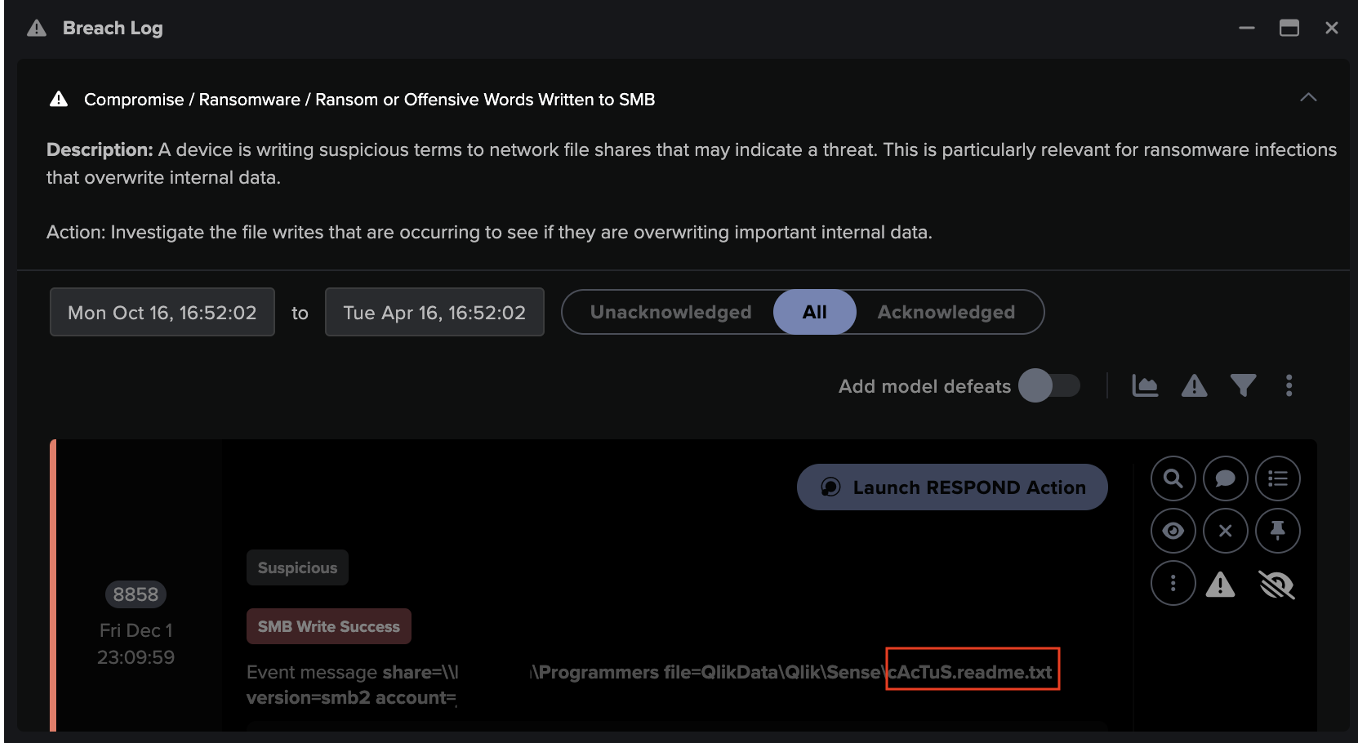
Four days following this observed activity, Darktrace’s AI detected the deployment of ransomware when multiple compromised devices began making anomalous SMB connections to file shares that they do not typically access, reading and writing similar volumes to the SMB file shares, as well as writing additional extensions to files over SMB. The file extension comprised a random string of letters and was likely to be unique to this target.
Using Darktrace, the customer obtained a full list of files that had been encrypted. The list included apparent financial records in an ‘Accounts’ file share.

Model breaches:
- Anomalous Connection / Unusual Incoming Data Volume
- Anomalous File / Internal / Additional Extension Appended to SMB File
- Compromise / Ransomware / Suspicious SMB Activity
- Compromise / Ransomware / SMB Reads then Writes with Additional Extensions
- Unusual Activity / Anomalous SMB Move & Write
- Unusual Activity / High Volume Server Data Transfer
- Unusual Activity / Sustained Anomalous SMB Activity
- Device / SMB Lateral Movement
Simultaneously, uploads of internal data to a rare external endpoint were observed within the network. The uploads were all performed using encrypted SSH/SFTP. In total, approximately 3.5GB of data was exfiltrated this way.
Despite the attacker using an encrypted channel to exfiltrate this data, Darktrace detected anomalous SMB file transfers prior to the external upload, indicating which files were exfiltrated. Here, Darktrace’s ability to go ‘back in time’ proved invaluable in helping analysts determine which files had been exfiltrated, although they were exfiltrated via an encrypted means.

Model breaches:
- Anomalous Server Activity / Outgoing from Server
- Compliance / SSH to Rare External Destination
- Unusual Activity / Enhanced Unusual External Data Transfer
- Device / Anomalous SMB Followed By Multiple Model Breaches
- Device / Large Number of Model Breaches
- Anomalous Connection / Uncommon 1 GiB Outbound
- Anomalous Connection / Data Sent to Rare Domain
- Anomalous Connection / Data Sent To New External Device
How did the attack bypass the rest of the security stack?
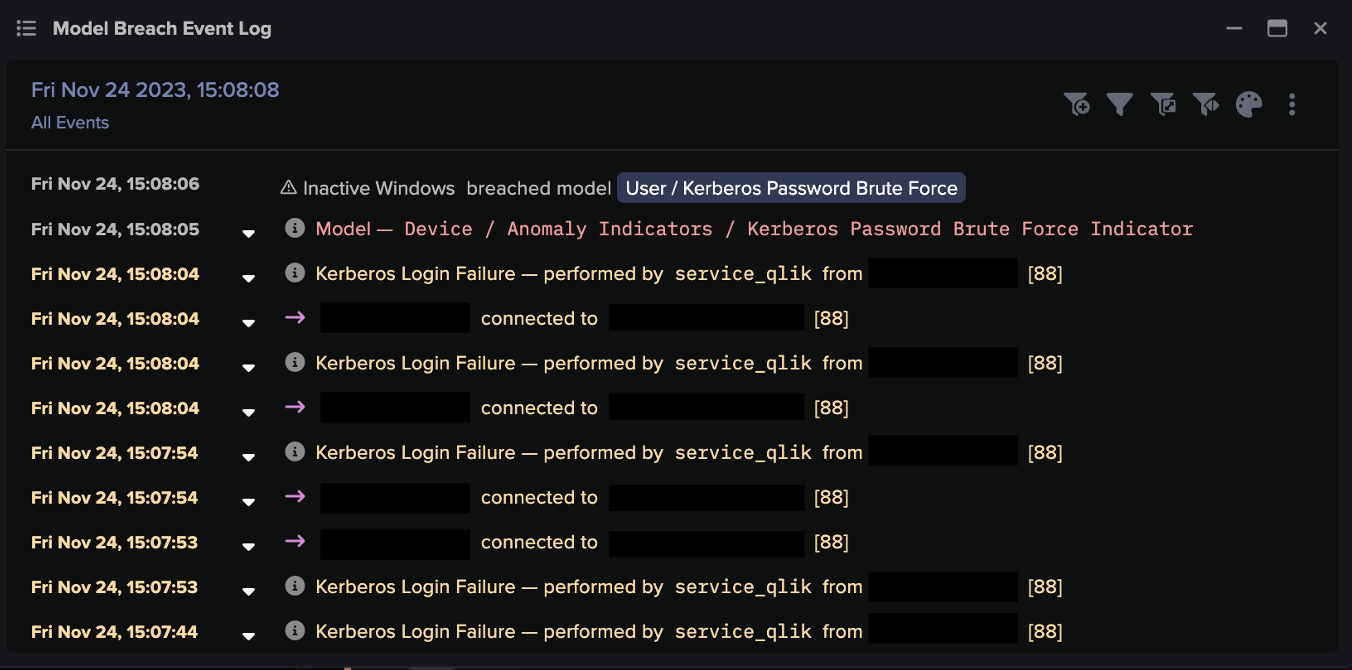
Existing administrative credentials were used to escalate privileges within the network and perform malicious activity.
Had Darktrace Antigena been active, it would have actioned a targeted, autonomous response to contain the activity in its early stages. Antigena would have enforced the ‘pattern of life’ on the devices involved in anomalous SMB activity — containing activity such as reading from file shares that are not normally connected, appending extensions to files and blocking outgoing connections to rare external endpoints.
However, in this case, Antigena was not set up to take action – it was configured in Human Confirmation mode. The incident was clearly alerted on by Darktrace, and appeared as a top priority item in the security team’s workflow. However, the security team was not monitoring Darktrace’s user interface, and in the absence of any action taken by other tools, the attack was allowed to progress, and the organization was obligated to disclose the details of the incident.
Streamlining the reporting process
In the modern threat landscape, leaning on AI to stop fast-moving and sophisticated attacks at machine speed and scale is critical. As this attack shows, the technology also helps organizations fulfill reporting requirements in the aftermath of an attack.
New legislation requires timely disclosure; with many traditional approaches to security, organizations do not have the capacity to surface the full details after an attack. On top of this, collating these details can take days or weeks. This is why Darktrace is no longer a nice-to-have but a must-have for critical infrastructure organizations, which are now required to report significant incidents swiftly.
Darktrace’s AI detects malicious activity as it happens and empowers customers to quickly understand the timeline of a compromise, as well as files accessed and exfiltrated by an attacker. This not only prepares organizations to resist the most sophisticated attacks, but also accelerates and radically simplifies the process of reporting the data breach.
Security teams should not have to confront disclosure processes on their own. Attacks happen fast, and their aftermaths are messy – retrospective investigation of lost data can be a futile effort with traditional approaches. With Darktrace, security teams can meet disruptive and sudden attacks with precise and nimble means of uncovering data, as well as detection and mitigation of risk. And, should the need arise, rapid and accurate reporting of events is laid out on a silver platter by the AI.
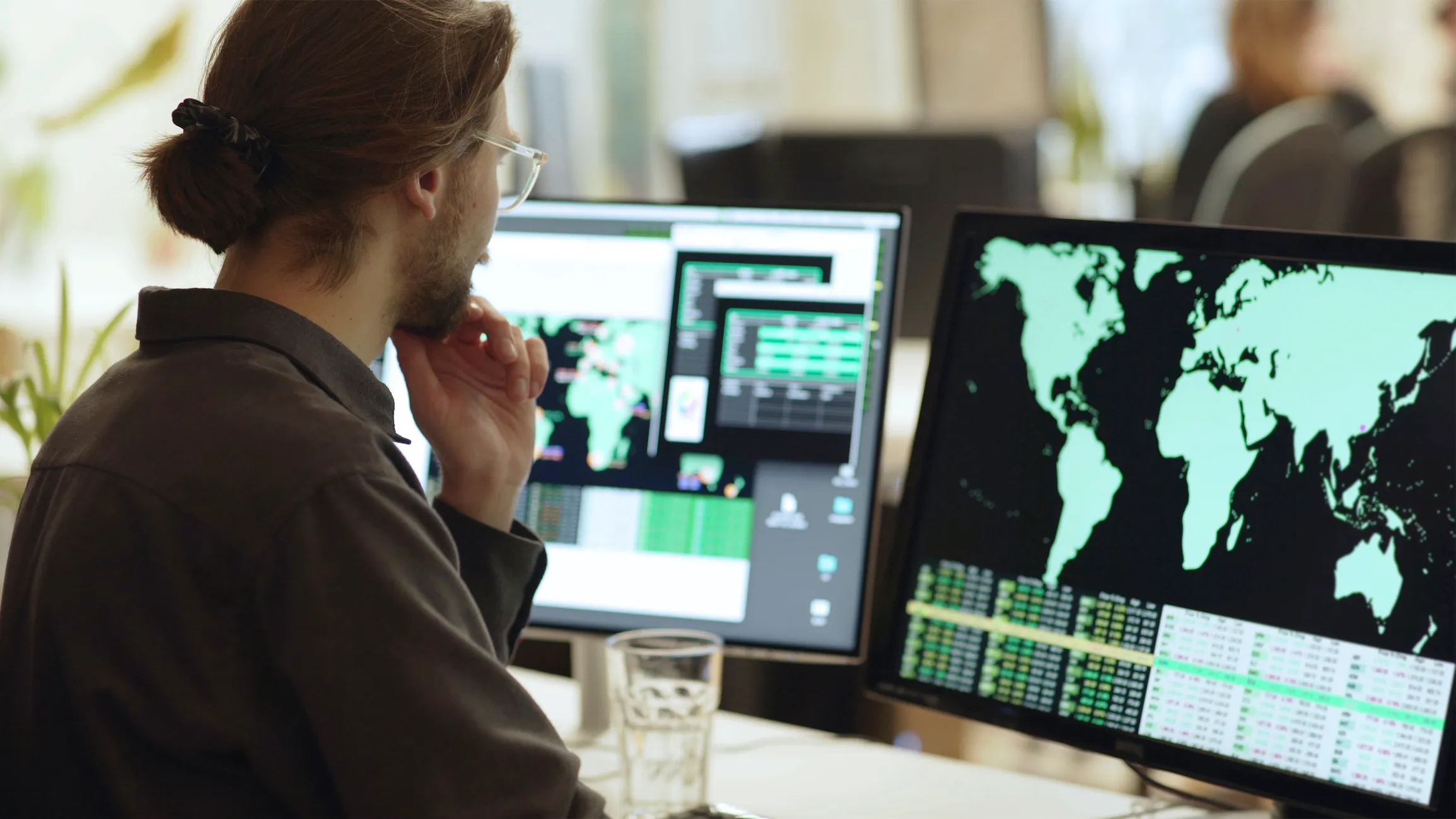

































![Cyber AI Analyst Incident Log showing the offending device making over 1,000 connections to the suspicious hostname “zohoservice[.]net” over port 8383, within a specific period.](https://assets-global.website-files.com/626ff4d25aca2edf4325ff97/662971c1cf09890fd46729a1_Screenshot%202024-04-24%20at%201.55.10%20PM.png)