As Arrow McLaren SP looks back on a positive season and prepares to build momentum into next year, Taylor Kiel (Team President) and Craig Hampson (Director of Trackside Engineering) reflect on key challenges and successes. With Pato O’Ward’s No. 5 car in the running to win the championship until the final race of the season, they reveal the formula for success – and how the team leverages AI and automation in every aspect of their work – from driver simulation to cyber security.
Data as the lifeblood for performance
In INDYCAR qualifiying, the difference between P1 and P10 can be as little as half a second, and when margins are that tight, the finer details in preparation make the difference. For us, that preparation is driven by data. Every race weekend and every practice session, over 100 lightweight sensors and several computers on the cars produce masses of data that is stored and analyzed for performance optimization.
This ecosystem includes an engine controller, a gear shift controller computer, and a computer unit that controls the clutch, and these systems all talk to each other across what is called a Controller Area Network (CAN). So the key question for us becomes: how do we get useful insights from that data, securely, and in a short period of time?
If you can think of something that’s happening on the car, the likelihood is our team is doing everything we can to try and measure it. Air speed, acceleration, tyre temperature, and so much more – we currently record over 1,500 data channels on the car itself, and we then process another 838 ‘math channels’ from combinations of this data – giving us, for example, the ride height of and downforce on the car.
This is more data than we can ever process with human beings alone, and a lot of our work now is figuring out how to automate these processes, using AI to look for patterns that humans simply cannot identify.
Pitting: More than just a tyre change
Each of our cars have two cellular-based telemetry systems built into them, but we are still limited on the amount of throughput we can observe real time, which is why we need to offload this data each time we pit during practice. This involves plugging in what we call an ‘umbilical cord’ that has a communication line and also powers the car.

Figure 1: A typical INDYCAR would last only minutes on its own battery without the engine running
Any typical race produces between 2.5GB and 3.3GB of data, in addition to in-car video, and a GPS system recording the car’s position on the track, which not only goes back to us but also to the relevant television broadcasters. So, we need to have a lot of storage available both in the cloud and on hard drives using a server. That data needs to be available not just to us at trackside but virtually to engineers not present at the race. And most importantly, that data needs to be secure, and protected from outside interference.
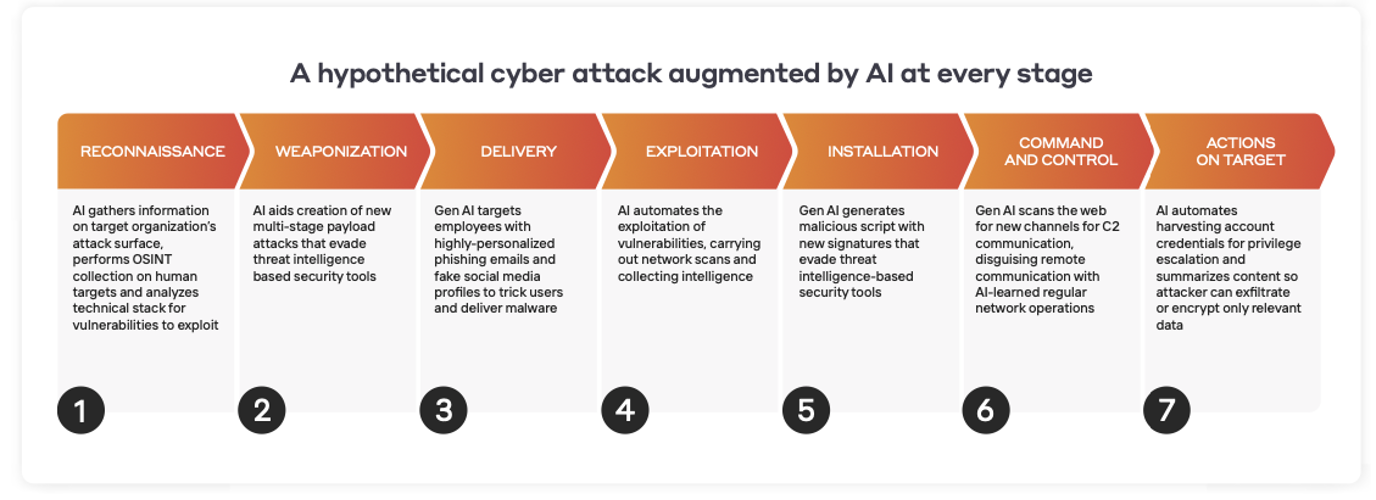
The cyber side: Turning to AI
All that precious data coming from the car, residing in the cloud or elsewhere in our organization, is susceptible to tampering from insiders and outsiders who may – deliberately or indirectly – compromise our ability to access or use that data reliably. As the cyber-threat landscape evolves – with ransomware bringing organizations of all shapes and sizes to a halt – we need to make sure we’re prepared for whatever attack is around the corner.
Firewalls, email gateways, and other perimeter protections are one part of the puzzle. But while these tools are focussed on keeping an attacker out – we needed another layer of defense that ensures that if these defenses are bypassed, we have an autonomous system that knows our organization inside out and can fight back on our behalf to disrupt emerging threats.
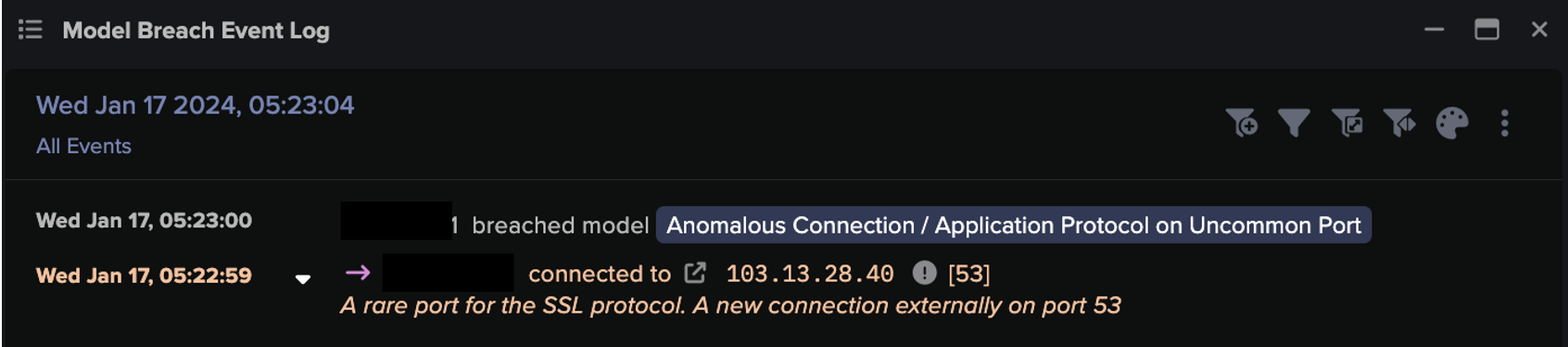
That’s where Darktrace has provided a revolutionary solution – using Self-Learning AI that understands every person and device from the ground up and identifies subtle deviations that point to a cyber-threat. And if ransomware strikes, 24/7 Autonomous Response is there in the form of Darktrace Antigena, taking precise action to contain ransomware and other threats at machine speed.
Double wins at doubleheaders
Using automation and AI throughout our technology stack enables us to extract meaningful insights from large pools of data and take quick, decisive action in the form of changes to the car or on-the-fly changes in race strategy.
The ability to react and react quickly is really put to the test on doubleheader race weekends, where any room for improvement you identify from Saturday’s race can be rectified in the form of overnight changes and implemented on Sunday. We believe it’s no coincidence that both of Pato’s No. 5 car’s wins came on the back end of doubleheader events, at Texas and Detroit Belle Isle. With people working in harmony with technology, our engineering team were able to make significant improvements to the car, react on the fly, and ultimately ensure we ended up ahead of the competition.
Digital fakes: Breaking new ground at Nashville
This year’s INDYCAR season featured a brand new track in Nashville, an exciting but daunting prospect for both the drivers and the team as a whole. Having access to a driver simulator, thanks to our partners at Chevrolet, we were able to run a virtual version of our car to try different setups, different techniques, and in this case have the driver learn his way round a whole new circuit.

Figure 2: The Chevrolet simulator projects a digital twin of the Nashville circuit
The track is recreated down to the nearest millimetre using a laser scanner, and then there is a lot of digital rendering involved, making it as realistic as possible with stands, fencing, and sponsor banners. Using this ‘digital fake’ representation was super helpful to the drivers in determining the correct approaches to corners, and for our engineers, enabling them to use the outputs to characterize the track.
The setup of the car in the simulator is effectively the same as the setup of the car in the real world: you set the spring rate and the ride height, it has the aerodynamic map, it knows the inertias and the masses of the car. It’s an incredibly complicated and powerful physics engine, but it gives us the ability to test things out in a controlled environment, and contributed toward one of Felix Rosenqvist’s strongest races of the season in the No. 7 car.
Simulations like these are the way of the future – not just for new circuits but in general. Rather than going through tyres and engines, we can replicate practice sessions in digital form, and the software gets closer to reality every day.
Looking ahead
What is next for Arrow McLaren SP? As we are now a part of the McLaren Racing family, new efficiencies and synergies are realized every month. We’ll certainly continue to leverage that valuable partnership, as well as our technology partnership with Darktrace, continuing to roll out their technology across our digital estate, including our email and cloud services.
In the INDYCAR Series, if you stay still, you go backwards, and the competition hots up every year. We know that now more than ever, the answer lies in using cutting-edge technologies across every aspect of the business to make our lives easier and ultimately propel us to the very top.