While cutting-edge technology is essential for organizations to secure their digital assets, having on-hand human support to deal with threats can be invaluable for lean security teams and organizations without Autonomous Response in their digital enterprise.
Cyber AI technology recently detected the QakBot banking trojan in a customer environment, and with the help of Darktrace’s SOC team, the customer was able to shut down the attack in under two hours.
QakBot malware
QakBot has built a name for itself over the past twelve years as one of the most deadly trojans in the game. Used in fast-paced, automated attacks against individual businesses, it has the ability to drain company resources and steal vast amounts of financial data. It is often downloaded during Emotet campaigns to infect devices and harvest bank account information.
Like other banking trojans, QakBot uses a dropper to install itself on a corporate device. It then self-propagates through a system and collects credentials at machine speed. Cyber-criminals can use this information to extract private data or distribute ransomware and further malicious payloads.
QakBot is extremely difficult for traditional security tools to detect. Due to a combination of its automatic worm-like capabilities, its use of a virus dropper with delayed execution, and several other obfuscation methods, it is able to bypass the majority of legacy tools and can lead to extreme financial repercussions if not dealt with in its initial stages.
The Darktrace SOC team
Darktrace’s Security Operations Center (SOC) team, located in Cambridge, San Francisco, and Singapore, deal with a wide range of these quick-moving and stealthy threats which are identified by Cyber AI, including ransomware deployments, SaaS account takeovers, and data exfiltration.
Such attacks often use ‘Living off the Land’ techniques which make them difficult to differentiate from legitimate network traffic. Moreover, many threat actors carry out malicious activities outside of a target organization’s normal working hours, amplifying the potential impact of a breach before it is discovered.
The Darktrace SOC team provides around-the-clock coverage of customer environments through Proactive Threat Notification (PTN) and Ask the Expert (ATE) services. Alongside autonomous AI detection, these services provide additional human monitoring and support for customers undergoing significant security events.
Uncovering the QakBot banking trojan

Figure 1: Timeline of the QakBot banking trojan attack, including the response from Darktrace’s services.
At a company in the EMEA region with around 7,000 devices, Cyber AI detected the early signs of a trojan horse. The organization did not have Antigena Email analyzing its email traffic in order to respond to attacks in the inbox, so when a phishing email slipped through the gateway and was opened by a user, their device began connecting to a high volume of suspicious endpoints.
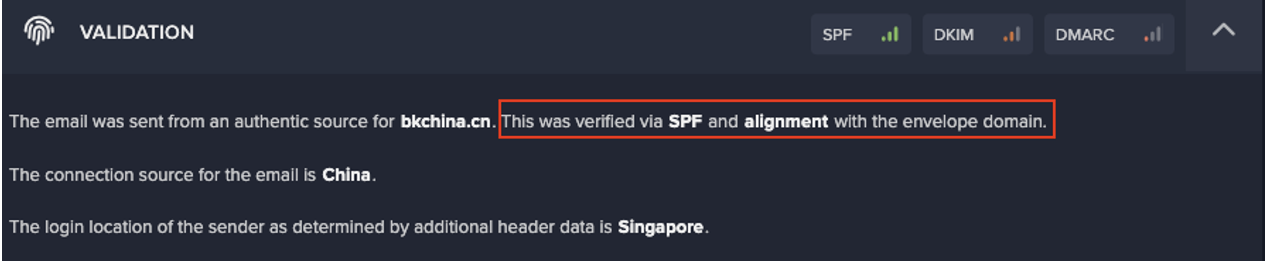
This resembled command and control (C2) communication, and, based on the unusual nature of this activity for the device and the environment, this behavior triggered multiple high scoring model breaches. One of these was a high fidelity model breach for ‘Suspicious SSL Activity’, which prompted an investigation through the Proactive Threat Notification service.

Figure 2: An example of the Cyber AI Analyst incident timeline for an infected device, showing command and control and reconnaissance activity.
An expert Darktrace analyst was alerted to the unusual connectivity by the Enterprise Immune System and began to investigate the anomalous behavior, determining that this device was exhibiting strong signs of a banking trojan infection. The analyst needed to move quickly: the trojan had immediately begun reconnaissance and was preparing to spread across the network.
Within an hour, the analyst had produced a brief report summarizing the activity and this was sent as a PTN alert to the customer. The report contained key technical information from the model breach and Cyber AI Analyst incident – including the timeframe, device hostname and IP address, suspicious external domains, and a reference for the customer to view this alert in the Darktrace UI.

Figure 3: Visual example of the Darktrace threat tray. In the QakBot attack, four Enhanced Monitoring model breaches were triggered, and these were investigated and alerted through the PTN service. They were all high scoring detections, clearly indicating a compromise.
Upon receiving the alert, the customer initiated further investigation and quickly shut down the affected device. The attack was contained in less than two hours.
Ask the Expert
After their initial remediation, the company reached out to the Darktrace team via Ask the Expert to confirm that this was a QakBot infection and to gain additional assistance in investigating the extent of the compromise.
The analyst team provided ongoing support to the investigation over the next six hours, concluding that this likely came from a phishing email and that no other devices in the environment were compromised. The analyst provided a list of observed Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) and worked with the customer to add these to the Darktrace Watched Domains List for further monitoring. The customer was also able to use this list to block the IoCs at the firewall.
The organization contained the infection, and no further suspicious behavior was observed from network devices.
Humans and AI
This case study is a perfect example of how Darktrace’s services provide constant assistance to customers every day of every week. On top of Darktrace’s advanced machine learning technology, the Darktrace SOC team serves as an additional layer of support for security teams of all sizes. Proactive Threat Notifications offer an extra set of eyes on emerging threats, while Ask The Expert provides a mechanism for customers to gain investigative support directly from Darktrace analysts.
The early detection of this banking trojan allowed the organization to deal with the threat before it could develop into a serious infection or a ransomware attack. QakBot is just one of many strains of swift self-spreading malware in today’s threat landscape. Such automated attacks consistently outpace the fastest of human defenders, exposing the desperate need for AI and autonomous systems to augment human teams and protect digital systems in real time.
If Antigena Network had been active in this environment, the suspicious external connectivity would have been blocked upon first detection, stopping the attack within seconds. In fact, the customer decided to deploy Antigena Network following this incident, and now benefits from 24/7 Autonomous Response against all emerging cyber-threats.
IoCs:
nerotimethod[.]com193[.]29[.]58[.]17345[.]32[.]211[.]20754[.]36[.]108[.]120144[.]139[.]166[.]1875[.]67[.]192[.]125 149[.]28[.]101[.]9037[.]211[.]90[.]17568[.]131[.]107[.]37162[.]222[.]226[.]194mywebscrap[.]com
Darktrace Modell-Erkennungen:
- Compromise / SSL or HTTP Beacon
- Compromise / Suspicious SSL Activity
- Device / Multiple C2 Model Breaches
- Device / Lateral Movement and C2 Activity
- Device / Multiple Lateral Movement Model Breaches
- Device / Large Number of Model Breaches
- Compromise / Suspicious Beaconing Behaviour
- Compromise / SSL Beaconing to Rare Destination
- Compromise / Slow Beaconing Activity To External Rare
- Compromise / High Volume of Connections with Beacon Score
- Anomalous Connection / Suspicious Self-Signed SSL
- Anomalous Connection / Rare External SSL Self-Signed
- Device / Reverse DNS Sweep
- Unusual Activity / Possible RPC Recon Activity
- Device / Active Directory Reconnaissance
- Device / Network Scan - Low Anomaly Score
- Anomalous Connection / SMB Enumeration